Isostructural coordination polymers: epitaxis vs. solid solution†
Abstract
Different synthetic conditions often afford different products and this is more evident for complex structures (i.e. solvates, polymorphs, co-crystals, solid solutions, etc.). We show how solution growth of a given set of components produces an epitaxial heterocrystal while mechanochemical synthesis yields a solid solution.
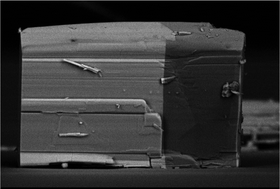
- This article is part of the themed collection: Dynamic behaviour and reactivity in crystalline solids

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...