Chromatographic determination of impurity binding affinities on biomineral crystals
Abstract
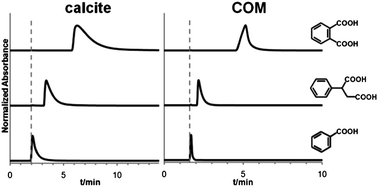
The feasibility and utility of a chromatographic approach for evaluating crystal growth modifiers were demonstrated. Relative binding affinities of impurity molecules on
- This article is part of the themed collection: Crystal Growth
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...