An organometallic derivative of a BAPTA ligand: towards electrochemically controlled cation release in biocompatible media†
Abstract
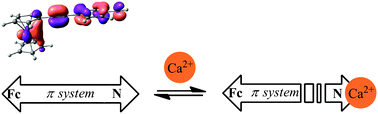
The combination of a
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Chemistry, UMR 8640 CNRS-ENS-UPMC, Ecole Normale Supérieure, 24 rue Lhomond, 75005 Paris, France
E-mail:
christian.amatore@ens.fr
Fax: +33 1-44323863
b Laboratoire Interfaces et Systèmes Electrochimiques-UPR 15, Universite Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 06, 75005 Paris, France
c Laboratoire d'Electrochimie Moléculaire, Université Paris Diderot, UMR CNRS 7591, 15 rue Jean de Baïf, 75013 Paris, France
The combination of a

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
K. X. Bhattacharyya, L. Boubekeur-Lecaque, I. Tapsoba, E. Maisonhaute, B. Schöllhorn and C. Amatore, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 5199 DOI: 10.1039/C1CC11081K
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
