An assay of DNA by resonance light scattering technique and its application in screening anticancer drugs†
Abstract
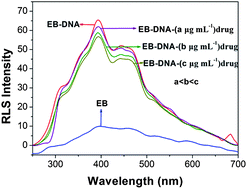
In this contribution, a novel assay has been developed to detect the interaction between DNA and drugs using ethidium bromide (EB) as a probe based on the decreased resonance light scattering (RLS) technique. It was found that, in pH 2.0 Britton–Robinson buffer solution, EB underwent dramatic enhancement of RLS signal when binding to DNA. Additionally, the strong RLS signal of the EB–DNA system was remarkably decreased after the addition of DNA-targeted anticancer drugs. The results showed a linear relationship between the enhanced RLS intensity of the EB–DNA system and concentration of DNA in the range of 0.015–40.8 μg mL−1. The linear regression equation is represented as follows: ΔIRLS = 4.15 + 21.14c with regression coefficient r = 0.9970 (n = 10). The detection limit was 0.3 ng mL−1. Only 2.0 × 10−8 mol L−1 was selected as the optimum EB concentration in this assay. Further study demonstrated that the anticancer efficacy of anticancer drugs varied inversely with RLS intensity of the EB–DNA-drug system. So, it is intuitive to see the sequence of antitumor efficiency of anticancer drugs without data processing by RLS screening spectra. Compared with the traditional cell-based screening methods, the proposed method was more convenient, rapid and intuitive. The reaction mechanism is discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Pharmaceutical Analysis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...