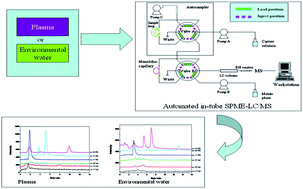
A weak anion exchange polymer monolith based on poly(4-vinylpyridine-co-ethylene dimethacrylate) (poly(VP-co-EDMA)) was prepared in the capillary. The use of polyethylene glycol (PEG) as porogens and EDMA as crosslinking monomers helps to increase the specific surface area and enhance hydrophobicity of the target monolith. The monolith exhibited satisfactory permeability, high mechanical strength and good stability in aqueous buffer. The potential application of the monolith as extraction medium in complicated samples has been demonstrated by in-tube solid-phase microextraction (in-tube SPME) of three non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (ketoprofen, fenbufen and ibuprofen) in human plasma and environmental water followed by on-line liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis. Integration of the sample extraction, LC separation and MS detection into a single system allowed for direct analysis of the NSAIDs in diluted plasma or environmental water sample, which facilitates the realization of automation of the sampling, extraction, separation and detection within a short period of time. The results showed that the limits of quantitation (S/N = 10) for the three NSAIDs were 6.70–15.9 ng mL−1 in human plasma and 0.65–1.87 ng mL−1 in water from East Lake. And the recoveries of the three NSAIDs spiked in human plasma and water from East Lake were from 88.17% to 112.48%, with relative standard deviations less than 13.87%. Compared to previously reported off-line sample extraction and conventional LC methods, the newly developed automated in-tube SPME/HPLC-MS in the current study provided a powerful tool for the fast and sensitive analysis of three NSAIDs in human plasma and environmental water.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...