Adsorption induced surface-stress sensing signal originating from both vertical interface effects and intermolecular lateral interactions
Abstract
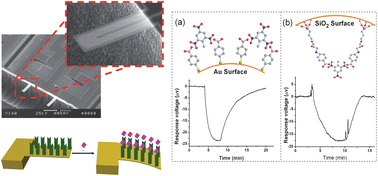
This research investigates the origin of specific molecule-
* Corresponding authors
a
State Key Lab of Transducer Technology, Science and Technology on Micro-system Lab, Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 865 Changning Road, Shanghai, P. R. China
E-mail:
xxli@mail.sim.ac.cn
Fax: +86 21 62513510
Tel: +86 21 62131794
b School of Digital Media, Jiangnan University, 1800 Lihu Avenue, Wuxi, Jiangsu Province, P. R. China
c School of Mechanical Systems Engineering, Chonnam National University, Gwang-Ju, Korea
This research investigates the origin of specific molecule-

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
T. Yang, X. Li, Y. Chen, D. Lee and G. Zuo, Analyst, 2011, 136, 5261 DOI: 10.1039/C1AN15695K
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
