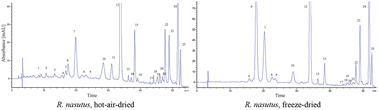
Rhinacanthus nasutus (L.) Kurz (Trade name: Bai he ling zhi), a traditional medicinal herb, has been reported to possess anticancer and antioxidant activities. However, the composition of the major functional compounds, carotenoids, remains uncertain. The objectives of this study were to develop a high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) method for carotenoid composition determination in R. nasutus and for carotenoid change by freeze-drying and hot-air-drying. A total of 24 carotenoids were separated within 54 min by using a YMC C30 column and a gradient mobile phase of methanol–acetonitrile–water (82 : 14 : 4, v/v/v) (A) and methylene chloride (100%) (B): 100% A initially, maintained for 10 min, decreased to 95% A in 25 min, 84% A in 30 min, 75% A in 37 min, 68% A in 40 min, 65% A in 47 min, and 55% A in 50 min with flow rate at 1 mL min−1 and detection wavelength at 450 nm. The various carotenoids were identified by comparing the retention time, absorption spectra, Q-ratio and mass spectra of unknown peaks with reference standards as well as photoisomerized standards. Quantitation was carried out using an internal standard β-apo-8′-carotenal, with all-trans-lutein and its cis isomers being present in the largest amount (862 μg g−1) in freeze-dried R. nasutus, followed by all-trans-violaxanthin (494 μg g−1), all-trans-β-carotene and its cis isomers (479 μg g−1), all-trans-neoxanthin and its cis isomers (251 μg g−1), all-trans-α-carotene and its cis isomers (85.2 μg g−1), luteoxanthin (14.3 μg g−1), all-trans-zeaxanthin (3.94 μg g−1), β-carotene-5,6-epoxide (3.45 μg g−1) and all-trans-β-cryptoxanthin (1.03 μg g−1). Comparatively, some more carotenoids including cis-violaxanthin, luteoxanthin, cis-neoxanthin, neochrome, 13- or 13′-cis-lutein, 9- or 9′-cis-lutein, β-carotene-5,6-epoxide, 9- or 9′-cis-β-carotene, 13- or 13′-cis-β-carotene, 15- or 15′-cis-β-carotene and 13- or 13′-cis-α-carotene were generated in R. nasutus during hot-air-drying.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...