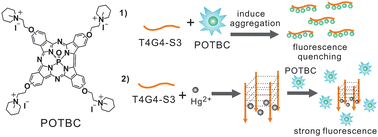
In the present work, a novel water-soluble cationic triazatetrabenzcorrole compound was synthesised. Its aggregation and fluorescence quenching properties are demonstrated by serval methods, such as UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopic studies and naked-eye visualization. Unlike the traditional Hg2+ sensor based on thymine–Hg2+–thymine, we use a novel approach, exploiting the high affinity of Hg2+ for sulfur in phosphorothioate DNA. Based on the S–Hg2+–S pairs, we designed the phosphorothioate DNA T4G4-S3 as an Hg2+ sensor, which can detect Hg2+ sensitively and selectively in aqueous solution. And this sensing system is fairly fast and convenient.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...