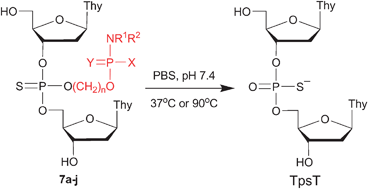
The hydroxyalkylated phosphoramidate 4a, phosphoramidothioates 4b, 4e–j, and phosphorodiamidothioates 4c and 4d have been identified as a new class of heat-sensitive thiophosphate protecting groups in the development of thermolytic immunomodulatory DNA prodrugs. These alcohols are converted to their deoxyribonucleoside phosphoramidite derivatives 6a–j, which are then used in the preparation of the thermosensitive dinucleoside phosphorothioates 7a–j. The negatively charged thiophosphate protecting groups of 7a–b and 7e–j presumably undergo thermolytic cyclodeesterification at elevated temperature under essentially neutral conditions. The thiophosphate protecting groups of 7e and 7f show relatively rapid deprotection kinetics at 37 °C (t½ = 20 and 42 h, respectively) and are therefore suitable for the protection of phosphodiester functions flanking the CpG motifs of immunomodulatory DNA sequences, whereas the thiophosphate protecting groups of 7g–j with thermolytic deprotection half-lives in the range of 94–265 h at 37 °C are more appropriate for the thiophosphate protection of CpG motifs. Furthermore, the thermostability of the group protecting the thiophosphate function of 7a (t½ = 82 min at 90 °C) should offer adequate protection of the 5′- and/or 3′-terminal phosphodiester functions of DNA prodrugs against ubiquitous extracellular and intracellular exonucleases.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...