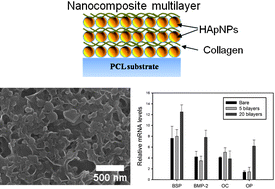
Three dimensional microstructured scaffolds with precisely defined architectures have many promising features for tissue engineering applications, such as controllable porosity, optimal mechanical strength, and adjustable contour fitting to a tissue defect site. However, for enhanced cell adhesion and differentiation, surface modified scaffolds with bioactive agents are additionally required. In this study, we present an osteogenic nanocomposite coating strategy on the surface of a microstructured scaffold for applications in bone tissue engineering. A layer-by-layer multilayer assembly method was employed to coat the scaffold surface with hydroxyapatite and collagen. The amount of the two components in the multilayer could be easily controlled by adjusting the number of deposition layers, leading to improved adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation of seeded mesenchymal stem cells. The hydroxyapatite/collagen nanocomposite coated scaffold showed enhanced osteogenic activities compared to bare scaffold, allowing great potential for bone regeneration.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...