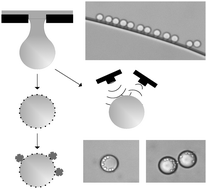
Quantitative targeted ultrasound contrast imaging demands for contrast agents with a small monodisperse size and a high coverage of specific ligands for effective adhesion under physiological shear stress conditions. However, the particles should also be large enough to generate sufficient ultrasound reflection. Standard perfluorocarbon emulsions do not satisfy both requirements (adhesion and echogenicity). Therefore, we decided to develop a membrane emulsification technique to produce echogenic monodisperse perfluorohexane emulsions able to carry specific ligands for adhesion to the artery wall. In this work, we demonstrate that membrane emulsification is an excellent tool to create strictly monodisperse echogenic perfluorohexane emulsions with a preset droplet size. Perfluorohexane is emulsified in water using photolithographic microsieves. An ultrasound experiment demonstrates that the perfluorohexane emulsions clearly enhance echogenicity. The acoustic enhancement varies with droplet size and surface coverage. The emulsions, with a biotinylated fluoro-surfactant, are able to bind avidin coated SiO2 particles. This proves that these emulsions show a very promising potential to act as key species in the field of selective targeting, which can provide novel insights into the development and early detection of important vascular diseases, e.g. atherosclerosis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...