Size-resolved analysis of fine and ultrafine particulate matter by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
Abstract
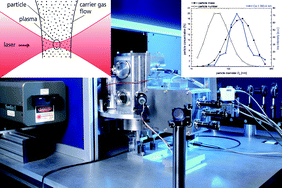
In emissions originating from industrial processes, elemental concentration characteristically depends on particle size. Therefore, not only is the average chemical composition of the particles in the focus of interest but also their size-dependent composition. For industrial applications such as on-line process control, a system using

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...