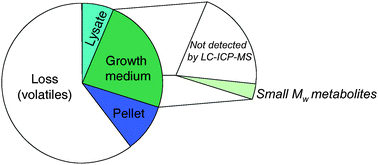
The aim of the present work was to estimate the amounts of selenium metabolites produced in a liver cell model. Five different selenium compounds comprising the inorganic selenium species selenate and selenite, methylseleninic acid (MeSeA) and the selenoamino acids, selenomethionine (SeMet) and Se-methylselenocysteine (Se-MeSeCys) were incubated in rat hepatocytes in amounts of 5 μM for 4 h. The distribution of selenium between media, lysate and insoluble fractions was determined by means of flow injection ICP-MS. Speciation analysis of growth media and lysate samples by LC-ICP-MS showed only limited metabolism of selenate, SeMet, and Se-MeSeCys, while MeSeA and selenite were extensively metabolized. Small molecule metabolites constituted less than 5% of the applied amount and some of the transformed selenium was detected in the protein fraction of the samples although all Se could not be accounted for. This result indicates that more important metabolism pathways may be related to protein bound selenium.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...