Cellulose conversion into alkylglycosides in the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride
Abstract
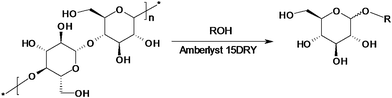
The conversion of cellulose into alkylglycosides is carried out in the ionic liquid
* Corresponding authors
a
Centre for Surface Chemistry and Catalysis, K.U. Leuven, Kasteelpark Arenberg 23 – box 02461, Heverlee, Belgium
E-mail:
dirk.devos@biw.kuleuven.be
Fax: +32 16321998
Tel: + 32 16321610
b Department of Chemistry, Coordination Chemistry, K.U. Leuven, Heverlee, Celestijnenlaan 200F – box 02404, Belgium
The conversion of cellulose into alkylglycosides is carried out in the ionic liquid

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
I. A. Ignatyev, P. G. N. Mertens, C. Van Doorslaer, K. Binnemans and D. E. de Vos, Green Chem., 2010, 12, 1790 DOI: 10.1039/C0GC00192A
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
