Continuous gas-phase desulfurisation using supported ionic liquid phase (SILP) materials
Abstract
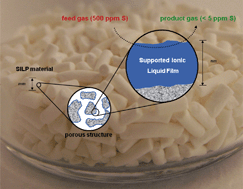
Supported ionic liquid phase (SILP) materials have been developed for a continuous gas cleaning process. The technology is exemplified for the desulfurisation of a model gas stream consisting of 500 ppmwt

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...