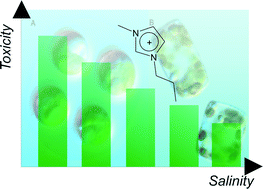
This paper reports on a detailed study of the influence of salinity on the biological activity of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium chlorides on two green algae Oocystis submarina and Chlorella vulgaris, one diatom Cyclotella meneghiniana and one blue-green alga Geitlerinema amphibium. All these organisms inhabit the Baltic Sea, an environment naturally varying greatly in salinity. The toxicity effects of ILs towards cyanobacterial and algal organisms were tested in fresh water and in water of four different salinities—8, 16, 24 and 32 PSU—reflecting the whole range encountered in the Baltic Sea. Increasing the salinity was found to exert a significant influence on ionic liquid toxicity in all cases. The lower toxicity is probably due to the reduced permeability of ionic liquid cations through the algalcell walls. Higher chloride concentrations offer a good ion-pairing environment for imidazolium cations, which therefore compete with hydroxyl or silanol functional groups in cell-wall structures. The results of this work indicate that at higher salinities algalgrowth is inhibited to a significantly lesser extent. With the same IL concentration, the toxicity decreases by eight–ten times in the algae or about three times in the cyanobacterium in the 0–32 PSU salinity range.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...