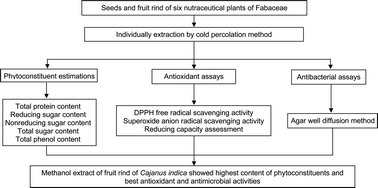
In the present study, the seeds and fruit rind of six plants of the Fabaceae family were selected to evaluate their potential as antioxidant and antibacterial agents. The dried powders were individually extracted with various organic solvents by the cold percolation method, were evaluated for antibacterial activity and methanol extracts used for antioxidant activities. Total phenol, protein and sugar contents were also measured. Antioxidant activities were measured by DPPH free radical scavenging activity, superoxide anion radical scavenging activity and reducing capacity assessment. Antibacterial activity was measured by the agar well diffusion method against four Gram positive and four Gram negative bacteria. The methanol extract of the fruit rind of C. indica showed the maximum DPPH free radical scavenging activity, superoxide anion radical scavenging activity, a high reducing capacity assessment and also had the highest total phenol content. There was a direct correlation between the phenol content and the antioxidant activity. The antibacterial activity of all the extracts was more pronounced on Gram positive bacteria than on Gram negative bacteria. Thus, the fruit rind of C. indica showed the best antioxidant and antibacterial activities.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...