Molecular mechanism of acid-triggered aryl–halide reductive elimination in well-defined aryl–CuIII–halide species†‡
Abstract
Well-defined aryl–
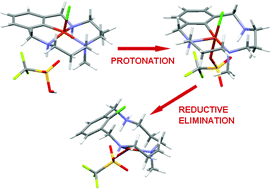
- This article is part of the themed collection: Dalton Discussion 12: Catalytic C–H and C–X bond activation (DD12)

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...