Direct amination of aryl halides with ammonia
Abstract
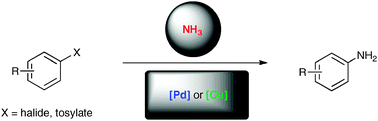
The traditional homogeneous access to
* Corresponding authors
a
Laboratoire de Chimie Moléculaire et Thioorganique, UMR 6507, INC3M, FR 3038, ENSICAEN-Université de Caen, 14050 Caen, France
E-mail:
jean-luc.renaud@ensicaen.fr
Fax: 33(0)231452877
b
Sciences Chimiques de Rennes, Catalyse et Organométalliques, UMR 6226, CNRS-Université de Rennes 1, Campus de Beaulieu, 35042 Rennes Cedex, France
E-mail:
cedric.fischmeister@univ-rennes1.fr
Fax: 33(0)223236939
c
Chimie ParisTech, UMR CNRS 7223, 11 rue Pierre et Marie Curie, 75231 Paris Cedex 05, France
E-mail:
christophe-thomas@chimie-paristech.fr
Fax: 33(0)223236939
The traditional homogeneous access to

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Y. Aubin, C. Fischmeister, C. M. Thomas and J. Renaud, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 4130 DOI: 10.1039/C003692G
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
