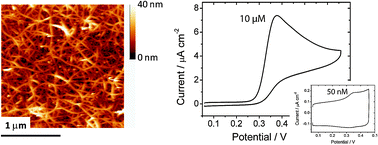
The characteristics of three different carbon electrodes, glassy carbon (GC), oxygen-terminated polycrystalline boron-doped diamond (pBDD) and “pristine” carbon nanotube networks (CNTN) as voltammetric sensors for detection of the neurotransmitter serotonin have been investigated. For each electrode, detection sensitivity was determined using cyclic voltammetry (CV), a technique often used to provide information on chemical identity in electrochemical assays. The CNTN electrodes were found to exhibit background current densities ca. two orders of magnitude smaller than the GC electrode and ca. twenty times smaller than pBDD, as a consequence of their “pristine” low capacitance and low surface coverage. This was a major factor in determining serotonin detection limits from CV, of 10 nM for the CNTN electrode, 500 nM for pBDD and 2 μM for GC. The two most sensitive electrodes (CNTN and pBDD) were further investigated in terms of resistance to electrode fouling. CV analysis showed that fouling was less on the pBDD electrode compared to the CNTN and, furthemore, for the case of pBDD could be significantly minimised by careful selection of the CV potential limits, in particular by scanning the electrode potential to suitably cathodic values after oxidation of the serotonin.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...