Chirality transition in the epoxidation of (−)-α-pinene and successive hydrolysis studied by Raman optical activity and DFT†
Abstract
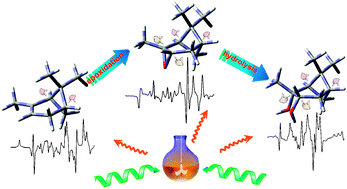
Characterization of the chirality evolution involved in chemical and biochemical reaction processes is extremely important to the understanding of the chiral catalysis mechanism. In this work, the chiral transition from the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...