Infrared spectra and quantum chemical characterization of weakly bound clusters of the benzoyl cation with Ar and H2O
Abstract
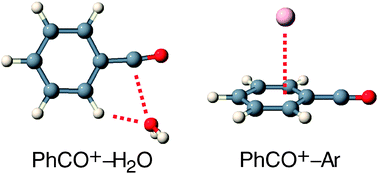
Weakly-bound ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) with smaller contributions of the
O) with smaller contributions of the ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O). This view is supported by the geometrical and vibrational properties of
O). This view is supported by the geometrical and vibrational properties of
- This article is part of the themed collection: Quantum molecular dynamics and control

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...