Isotopic effect and temperature dependent intramolecular excitation energy transfer in a model donor–acceptor dyad
Abstract
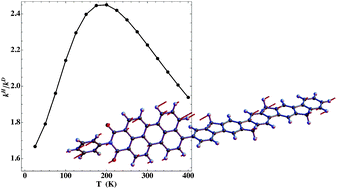
We consider here the non-adiabatic energy transfer dynamics for a model bi-
- This article is part of the themed collection: Electronic energy transfer

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...