Characterisation of the membrane affinity of an isoniazidepeptide conjugate by tensiometry, atomic force microscopy and sum-frequency vibrational spectroscopy, using a phospholipid Langmuir monolayer model†
Abstract
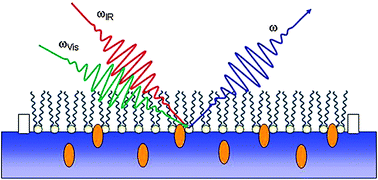
* Corresponding authors
a
Laboratory of Interfaces and Nanostructures, Institute of Chemistry, Eötvös Loránd University, P.O. Box 32, Budapest 112, Hungary
E-mail:
kisseva@chem.elte.hu
b Research Group of Peptide Chemistry, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Eötvös Loránd University, POB 32, Budapest 112, Hungary
c Department of Organic Chemistry, Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary
d
Chemical Research Center, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Pusztaszeri út 59-67, H-1025 Budapest, Hungary
E-mail:
ktamas@chemres.hu

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
K. Hill, C. B. Pénzes, D. Schnöller, K. Horváti, S. Bősze, F. Hudecz, T. Keszthelyi and É. Kiss, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 11498 DOI: 10.1039/C002737E
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
