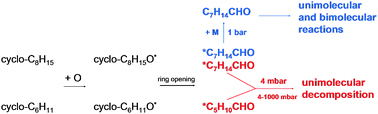
The kinetics of cycloalkyl + O reactions were studied with respect to their rate coefficients and the product branching ratios from the decomposition of the chemically activated cycloalkoxy radicals. Rate coefficients for the reactions of cyclohexyl (c-C6H11), cycloheptyl (c-C7H13) and cyclooctyl (c-C8H15) radicals with oxygen atoms were determined with an experimental setup consisting of a discharge flow reactor with molecular beam sampling and REMPI/TOF-MS detection. The following rate coefficients were obtained (units: cm3/mol−1 s−1): k(c-C6H11 + O) = (1.33 ± 0.24) × 1014(T/298 K)0.11 (T = 250–600 K), k(c-C7H13 + O) = (1.85 ± 0.25) × 1014 (T = 298 K), k(c-C8H15 + O) = (1.56 ± 0.20) × 1014(T/298 K)0.66±0.15 (T = 268–363 K). Stable products were determined by quantitative FTIR spectroscopy. The decomposition of the cycloalkoxy radicals leads besides β-C–H bond fission (yields: 24% for c-C6H11O, 20–25% for c-C8H15O) mainly to alkyl radicals by ring-opening via β-C–C bond cleavage. These open-chain alkyl radicals further decompose mainly by β-C–C bond scission. An increase of the total pressure from 4 mbar to 1 bar had no effect on the product distribution for the reaction c-C6H11 + O, whereas for the reaction c-C8H15 + O further decomposition of the ring-opening product is significantly suppressed at 1 bar. The experimental results on the channel branching and its pressure dependence were rationalized with the statistical rate theory. A comparison of the experimental and modeling results indicates a significant influence of hindered internal rotations (HIRs) on the reactions of the ring-opening products. The harmonic approximation to describe these modes was shown to be inadequate, while a treatment as one-dimensional HIRs led to a significantly improved agreement between experimental and modeling results. Implications of our findings for the formation of secondary organic aerosol and high-temperature combustion are discussed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...