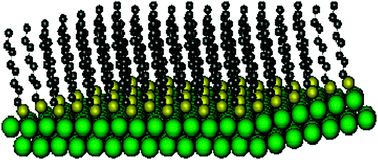
Model non-equilibrium molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are presented of heat transfer from a hot Au {111} substrate to an alkylthiolate self-assembled monolayer (H-SAM) to assist in obtaining an atomic-level understanding of experiments by Wang et al. (Z. Wang, J. A. Carter, A. Lagutchev, Y. K. Koh, N.-H. Seong, D. G. Cahill, and D. D. Dlott, Science, 2007, 317, 787). Different models are considered to determine how they affect the heat transfer dynamics. They include temperature equilibrated (TE) and temperature gradient (TG) thermostat models for the Au(s) surface, and soft and stiff S/Au(s) models for bonding of the S-atoms to the Au(s) surface. A detailed analysis of the non-equilibrium heat transfer at the heterogeneous interface is presented. There is a short time temperature gradient within the top layers of the Au(s) surface. The S-atoms heat rapidly, much faster than do the C-atoms in the alkylthiolate chains. A high thermal conductivity in the H-SAM, perpendicular to the interface, results in nearly identical temperatures for the CH2 and CH3 groups versus time. Thermal-induced disorder is analyzed for the Au(s) substrate, the S/Au(s) interface and the H-SAM. Before heat transfer occurs from the hot Au(s) substrate to the H-SAM, there is disorder at the S/Au(s) interface and within the alkylthiolate chains arising from heat-induced disorder near the surface of hot Au(s). The short-time rapid heating of the S-atoms enhances this disorder. The increasing disorder of H-SAM chains with time results from both disorder at the Au/S interface and heat transfer to the H-SAM chains.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...