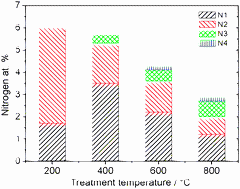
Nitrogen-containing functional groups were generated on the surface of partially oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) via post-treatment in ammonia. The treatment temperature was varied in order to tune the amount and type of nitrogen- and oxygen-containing functional groups, which were studied using high-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and temperature-programmed desorption (TPD). The surface defects on CNTs due to the incorporation of nitrogen were investigated by Raman spectroscopy. Deconvoluted XP N1s spectra were used for the quantification of different nitrogen-containing functional groups, and TPD studies were performed in inert and ammonia atmosphere to investigate the surface reactions occurring on the oxidized CNT surfaces quantitatively. Nitrile, lactam, imide and amine-type functional groups were formed in the presence of ammonia below 300 °C. When the OCNTs were treated in the medium temperature range between 300 °C to 500 °C, mainly pyridine-type nitrogen groups were generated, whereas pyridinic, pyrrolic and quaternary-type nitrogen groups were the dominating species present on the CNT surface when treated above 500 °C. It was found that about 38% of the oxygen functional groups react with ammonia below 500 °C.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...