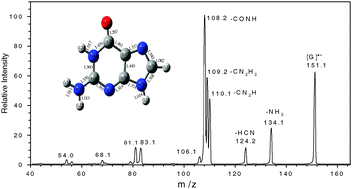
Gas-phase guanine (G) radical cations were generated by electrospraying a solution of guanosine (L) and Cu(NO3)2. Collision-induced dissociation (CID) for guanine radical cations yielded five competing dissociation channels, corresponding to the elimination neutral molecules of NH3, HCN, H2NC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N (HN
N (HN![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH), HNCO and the neutral radical ˙N
NH), HNCO and the neutral radical ˙N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH, respectively. The primary product ions were further characterized by their relevant fragmentions. Ab initio and density functional theory (DFT) calculations were employed to explain the experimental observations. Ten stable radical cation isomers were optimized and the potential energy surfaces (PESs) for the isomerization processes were explored in detail. Starting with the most stable isomer, the primary dissociation channels of guanine radical cations were theoretically investigated. DFT calculations show that the energy barriers for the eliminations of NH3, HCN, H2NC
NH, respectively. The primary product ions were further characterized by their relevant fragmentions. Ab initio and density functional theory (DFT) calculations were employed to explain the experimental observations. Ten stable radical cation isomers were optimized and the potential energy surfaces (PESs) for the isomerization processes were explored in detail. Starting with the most stable isomer, the primary dissociation channels of guanine radical cations were theoretically investigated. DFT calculations show that the energy barriers for the eliminations of NH3, HCN, H2NC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N (HN
N (HN![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH), HNCO and ˙N
NH), HNCO and ˙N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH are 397 kJ mol−1, 479 kJ mol−1, 294 kJ mol−1 (298 kJ mol−1), 306 kJ mol−1, and 275 kJ mol−1, respectively. The results are consistent with the energy-resolved CID of guanine radical cation, in which the eliminations of NH3 and HCN are less abundant than the other channels.
NH are 397 kJ mol−1, 479 kJ mol−1, 294 kJ mol−1 (298 kJ mol−1), 306 kJ mol−1, and 275 kJ mol−1, respectively. The results are consistent with the energy-resolved CID of guanine radical cation, in which the eliminations of NH3 and HCN are less abundant than the other channels.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N (HN
N (HN![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH),
NH), ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH, respectively. The primary product ions were further characterized by their relevant fragmentions.
NH, respectively. The primary product ions were further characterized by their relevant fragmentions. ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N (HN
N (HN![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH),
NH), ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH are 397 kJ mol−1, 479 kJ mol−1, 294 kJ mol−1 (298 kJ mol−1), 306 kJ mol−1, and 275 kJ mol−1, respectively. The results are consistent with the energy-resolved
NH are 397 kJ mol−1, 479 kJ mol−1, 294 kJ mol−1 (298 kJ mol−1), 306 kJ mol−1, and 275 kJ mol−1, respectively. The results are consistent with the energy-resolved 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...