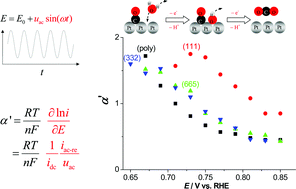
The apparent transfer coefficient, which gives the magnitude of the potential dependence of the electrochemical reaction rates, is the key quantity for the elucidation of electrochemical reaction mechanisms. We introduce the application of an ac method to determine the apparent transfer coefficient α′ for the oxidation of pre-adsorbed CO at polycrystalline and single-crystalline Pt electrodes in sulfuric acid. The method allows to record α′ quasi continuously as a function of potential (and time) in cyclic voltammetry or at a fixed potential, with the reaction rate varying with time. At all surfaces (Pt(poly), Pt(111), Pt(665), and Pt(332)) we clearly observed a transition of the apparent transfer coefficient from values around 1.5 at low potentials to values around 0.5 at higher potentials. Changes of the apparent transfer coefficients for the CO oxidation with potential were observed previously, but only from around 0.7 to values as low as 0.2. In contrast, our experimental findings completely agree with the simulation by Koper et al., J. Chem. Phys., 1998, 109, 6051–6062. They can be understood in the framework of a Langmuir–Hinshelwood mechanism. The transition occurs when the sum of the rate constants for the forward reaction (first step: potential dependent OH adsorption, second step: potential dependent oxidation of COad with OHad) exceeds the rate constant for the back-reaction of the first step.
We expect that the ac method for the determination of the apparent transfer coefficient, which we used here, will be of great help also in many other cases, especially under steady conditions, where the major limitations of the method are avoided.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...