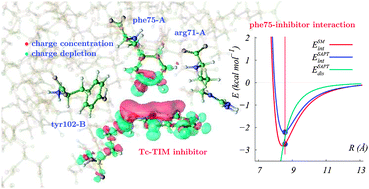
The interaction between selected amino acid residues of the homodimeric enzyme triosephosphate isomerase from Trypanosoma cruzi with the inhibitor 3-(2-benzothiazolylthio)-1-propanesulfonic acid (BTT) was investigated by means of high level quantum chemical methods. The amino acids phe75A, arg71A and tyr102B from the enzyme monomers A and B were selected using experimental X-ray structural data. The ab initio intermolecular energies for the association of the inhibitor with the individual amino acids were calculated in two forms, namely, with a supermolecular approach and using the symmetry adapted perturbation theory. The latter also provided the contributions to the interaction energies, which were interpreted in terms of the usual van der Waals forces. The electron density for the specific interactions between BTT and the amino acids and the charge redistribution due to complex formation were also analyzed. It was found that for phe75A and tyr102B the dispersion energy is the dominant contribution to the complex stabilization followed by the induction and electrostatic energies. In addition, whereas the face-edge complex of BTT with phe75A exhibits a C–H π bond similar to that observed for the benzene dimer, the complex with arg71A shows an important charge redistribution on the amino acid in regions far removed from those where the intermolecular specific interactions occur.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...