Low temperature rate coefficients for reactions of the butadiynyl radical, C4H, with various hydrocarbons. Part I: reactions with alkanes (CH4, C2H6, C3H8, C4H10)
Abstract
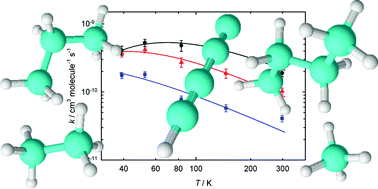
The kinetics of the reactions of the linear
* Corresponding authors
a
Institut de Physique de Rennes, Equipe Astrochimie Expérimentale UMR 6251 du CNRS-Université de Rennes 1, Bât. 11c, Campus de Beaulieu, 35042 Rennes Cedex, France
E-mail:
ian.sims@univ-rennes1.fr; sebastien.le-picard@univ-rennes1.fr
The kinetics of the reactions of the linear

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
C. Berteloite, S. D. Le Picard, N. Balucani, A. Canosa and I. R. Sims, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 3666 DOI: 10.1039/B907154G
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
