A microfluidic approach for high-throughput droplet interface bilayer (DIB) formation†
Abstract
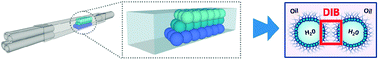
We present a simple, automated method for high-throughput formation of droplet interface bilayers (DIBs) in a microfluidic device. We can form complex DIB networks that are able to fill predefined three dimensional architectures. Moreover, we demonstrate the flexibility of the system by using a variety of lipids including

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...