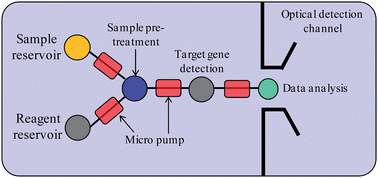
The rapid diagnosis of various diseases is a critical advantage of many emerging biomedical tools. Due to advances in preventive medicine, tools for the accurate analysis of genetic mutation and associated hereditary diseases have attracted significant interests in recent years. The entire diagnostic process usually involves two critical steps, namely, sample pre-treatment and genetic analysis. The sample pre-treatment processes such as extraction and purification of the target nucleic acids prior to genetic analysis are essential in molecular diagnostics. The genetic analysis process may require specialized apparatus for nucleic acid amplification, sequencing and detection. Traditionally, pre-treatment of clinical biological samples (e.g. the extraction of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA)) and the analysis of genetic polymorphisms associated with genetic diseases are typically a lengthy and costly process. These labor-intensive and time-consuming processes usually result in a high-cost per diagnosis and hinder their practical applications. Besides, the accuracy of the diagnosis may be affected owing to potential contamination from manual processing. Alternatively, due to significant advances in micro-electro-mechanical-systems (MEMS) and microfluidic technology, there are numerous miniature systems employed in biomedical applications, especially for the rapid diagnosis of genetic diseases. A number of advantages including automation, compactness, disposability, portability, lower cost, shorter diagnosis time, lower sample and reagent consumption, and lower power consumption can be realized by using these microfluidic-based platforms. As a result, microfluidic-based systems are becoming promising platforms for genetic analysis, molecular biology and for the rapid detection of genetic diseases. In this review paper, microfluidic-based platforms capable of identifying genetic sequences and diagnosis of genetic mutations are surveyed and reviewed. Some critical issues with the use of microfluidic-based systems for diagnosis of genetic diseases are also highlighted.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...