Thermodynamic profile for urea photo-release from a N-(2-nitrobenzyl) caged urea compound
Abstract
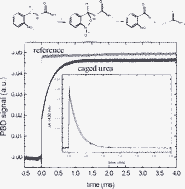
Photoactivable bioactive molecules, often termed “caged” compounds, have attracted significant attention as useful tools for photo-regulating enzymatic activity. Here we examine the mechanism associated with photo-release of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...