Understanding the mechanism of polar Diels–Alder reactions
Abstract
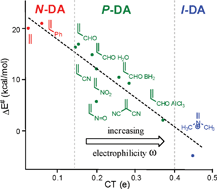
A good correlation between the activation energy and the polar character of Diels–Alder reactions measured as the charge transfer at the transition state structure has been found. This electronic parameter controls the reaction rate to an even greater extent than other recognized structural features. The proposed polar mechanism, which is characterized by the electrophilic/nucleophilic interactions at the transition state structure, can be easily predicted by analyzing the electrophilicity/nucleophilicity indices defined within the conceptual density functional theory. Due to the significance of the polarity of the reaction, Diels–Alder reactions should be classified as non-polar (N), polar (P), and ionic (I).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...