The biosynthesis of polyketide-derived polycyclic ethers†
Abstract
Covering: up to 2008
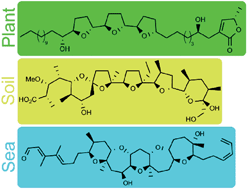
The biosynthetic pathways to polyketide-derived polycyclic ethers, in bacteria, plants and marine organisms, have, until now, tended to be considered separately. The purpose of this article is to provide an integrated review of the common mechanistic aspects of polyether biosynthesis from these diverse sources. In particular, the focus will be on the proposed mechanisms of oxidative cyclisation, as well as on the known differences in polyketide chain construction between the terrestrial and marine polyethers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...