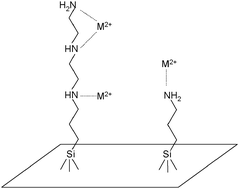
A synthesized crystalline lamellar sodium RUB-18 was reacted with hydrochloric acid solution to exchange the original hydrated sodium cation on the interlayer space to obtain the acidic form, H-RUB-18, whose silanol groups on the surface favour covalent bond formation with the silylating agents 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (N) and N-3-trimethoxysilylpropyldiethylenetriamine (3N). Both new organofunctionalized nanostructured materials were characterized by means of elemental analysis, IR spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction patterns, NMR, thermogravimetry and scanning electron microscopy. The determined maximum amount of coupling reagents incorporated were 2.28 and 1.03 mmol g−1, for RUB-N and RUB-3N, respectively. The H-RUB-18 basal distance of 0.75 nm expands to 0.94 and 1.10 nm in two successive steps of reaction. Covalent bond formation between the organosilyl groups and the inorganic layered backbone was confirmed by 13C and 29Si NMR, as evidenced by carbon chemical shifts of the pendant organic chains and by the Q3 and Q4 sites, in addition to T2 and T3 species, that correspond to carbon–silicon bond formation from the pendant coupling reagents covalently attached to the H-RUB-18 structure. These two new synthesized materials have the ability to extract divalent cations from aqueous solution, using a batchwise process. The same interaction was also followed through calorimetric titration and the thermodynamic data, with high entropic contributions, indicated favourable cation/basic centre interactions at the solid/liquid interface.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...