Identification of anionic selenium species in Se-rich yeast by electrospray QTOF MS/MS and hybrid linear ion trap/orbitrapMSn†
Abstract
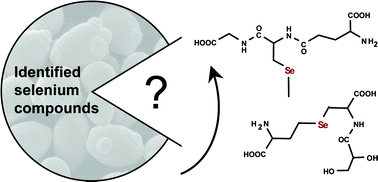
An analytical approach allowing the identification of unknown selenium
* Corresponding authors
a Department of Applied Chemistry, Corvinus University of Budapest, 1118 Budapest, Villányi út 29-33, Hungary
b
Laboratoire de Chimie Analitique, Bio-inorganique et Environnement, UMR 5254, Hélioparc, 2av. Pr, Angot, F-64053 Pau, France
E-mail:
ryszard.lobinski@univ-pau.fr
Fax: +33 559-407781
Tel: +33 559-407755
c Department of Analytical Chemistry, Warsaw University of Technology, 00-664 Warszawa, Poland
An analytical approach allowing the identification of unknown selenium

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
