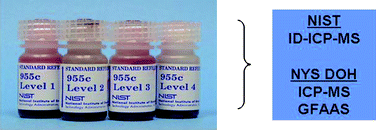
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed Standard Reference Material (SRM) 955c, a new caprine-based, four-level blood standard with certified blood lead levels (BLLs) ranging from 0.4 µg/dL (0.02 µmol/L) Pb to 45 µg/dL (2.2 µmol/L) Pb. Certified values are based on ID-ICP-MS. Strict control and accurate measurement of the procedure blank were necessary to minimize uncertainty for the lowest level (Level 1) and obtain a relative expanded uncertainty (k = 2) of 2.6%. Level 1 is intended to represent a baseline BLL and provides a means to define detection levels and validate methods developed to measure lead at background environmental levels in blood. Level 2 is near 10 µg/dL (0.48 µmol/L), the current threshold defined by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for public health action and clinical follow up. The standard has been developed in collaboration with the Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health, which provided measurements based on GFAAS and ICP-MS. Results from these clinical methods are statistically compared to the Isotope Dilution (ID) values. The Level 1 SRM 955c standard is below the detection limit of the GFAAS method, but comparison of Level 1 results for the ICP-MS method with the ID-ICP-MS values shows no evidence of statistically significant disagreement, suggesting that the ICP-MS method appears capable of measuring BLLs at background concentrations. Comparison of both GFAAS and ICP-MS results with the ID ICP-MS values for the Level 2 through Level 4 SRM 955c standards similarly shows no statistically significant disagreement between methods at these elevated blood Pb levels. In addition to the SRM 955c data, long-term method performance data are presented for SRM 955b Lead in Bovine Blood and for SRM 966 Toxic Elements in Bovine Blood. The clinical methods performed well within CLIA guidelines for these materials; however, a small negative bias for the ICP-MS value relative to the certified value for SRM 966 requires further investigation.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...