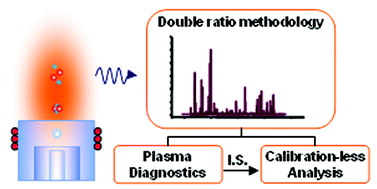
Towards a calibration-less ICP-AES method for the determination of trace elements in aqueous solutions: Double ratio plasma diagnostics combined with an internal standard†
Abstract
We propose a calibration-less approach to determine the concentration of the analytes in a solution in

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...