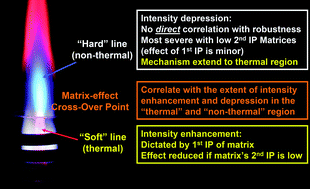
The dependence of matrix-effect cross-over locations on plasma operating conditions (central-channel gas flow, plasma forward power, and dry/wet plasma), excitation potentials of emission lines, and matrix properties was explored. Improving plasma robustness either by lowering the central-channel gas flow rate, by increasing the plasma forward power or by employing a plasma torch with a larger injector diameter either does not significantly reduce or occasionally only slightly reduces the depressive matrix effect in the normal analytical zone (NAZ) of the plasma caused by matrix elements with a low second ionization potential. Aqueous aerosols were found to have a large impact on the location of the cross-over point; cross-over locations can be 7 mm apart when dry and wet plasma conditions are used. Further, the location of a cross-over point is sandwiched between the peak emission locations of “soft” and “hard” emission lines, which correspond to thermal and non-thermal regions of the plasma, respectively. Cross-over points were found to shift downward almost linearly with increasing first ionization potentials of the matrices. The first ionization potential of the matrix was found also to be the prime parameter that defines the magnitude of emission enhancement low in the plasma. In contrast, it is the second ionization potential of the matrix element that dictates the magnitude of signal depression high in the plasma. The locations of cross-over points correlate strongly with the magnitude of the depression in the normal analytical zone of the plasma. In addition, the mechanism(s) responsible for this depressive effect was found to be operative at all vertical heights in the plasma, including the emission enhancement region low in the discharge.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...