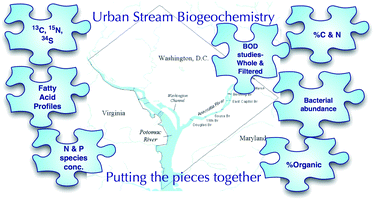
The Anacostia River in Washington, D.C., USA is an urban waterway contaminated with PAHs, PCBs, metals and sewage. Although several studies have examined the heavy metal geochemistry within the river, no studies have examined basic biogeochemical processes within the Anacostia river system. This study examines nutrients, bacterial biomarkers, organic material, and carbon, nitrogen and sulfur sources in the system. High biological oxygen demand and low nitrogen (0.33–0.56 mg L−1) and phosphorus (0.014–0.021 mg L−1) concentrations were observed in three areas of the river. Downstream sites had higher nutrient concentrations and dissolved organic matter (up to 13.7 mg L−1). Odd-chain length and branched fatty acids (FAs) in the sediments indicated bacterial sources, but long chain FAs indicative of terrestrial primary production were also abundant in some sediments. Sediment carbon stable isotope analyses showed a mix of autochthonous and allochthonous derived materials, but most carbon was derived from terrestrial sources (−23.3 to −31.7‰). Sediment nitrogen stable isotopes ranged from −5.4 to 5.6‰, showing nitrate uptake by plants and also recycling of nitrogen within the river. Sulfur sources were generally between 3 and −5‰, reflecting local sulfate sources and anaerobic sulfate reduction.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...