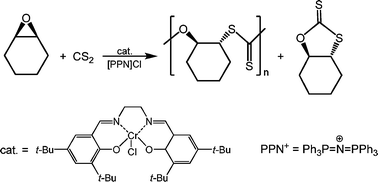
The synthesis of poly(thiocarbonates) has been achieved via the (salen)CrCl/[PPN]Cl (salen = N,N′-bis(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylidene)-1,2-ethylenediamino) and PPN+ = bis(triphenyl-phosphoranylidene)ammonium) catalyzed coupling of carbon disulfide and cyclohexene oxide. Optimal catalytic activity was observed at 50 °C and a 1 : 1 carbon disulfide to cyclohexene oxide loading ratio to afford copolymers with molecular weights ranging from 14 000–34 000 g mol−1 with narrow molecular weight distributions. The exchange of sulfur and oxygen atoms was observed in both the copolymer and cyclic products. In situ infrared monitoring of the coupling reactions revealed an initiation period followed by formation of copolymers enriched in oxygen content, and concomitantly cyclic thiocarbonates enriched in sulfur content. By way of contrast, the copolymerization of cyclohexene sulfide and carbon disulfide was found to be highly selective and effective for producing cyclohexylene trithiocarbonate vs. the all-sulfur copolymer at 30 °C. Density functional theory calculations were carried out on the possible cyclic materials from the coupling of cyclohexene oxide and CS2, which revealed cyclohexylene trithiocarbonate to be the most stable cyclic species.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...