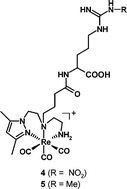
Aiming to design radioactive compounds based on the core “99mTc(CO)3” for probing inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) levels in vivo, we have synthesized conjugates containing a pyrazolyl-diamine chelating unit and pendant L-arginine analogues (substrates and inhibitors of NOS). Reaction of the conjugates with fac-[M(CO)3]+ (M = Re, 99mTc) gave bioorganometallic complexes of the type fac-[M(CO)3(k3-L)] in good yield. After in vitro testing using the oxyhemoglobin NO capture assay, we concluded that the affinity of the inhibitor-containing conjugates to iNOS seems to be less affected upon metallation with rhenium than the substrate-containing conjugates. The complexes bearing guanidino substituted analogues of L-arginine still present considerable inhibitory action (Nω-monomethyl-L-arginine, Ki = 36 μM; Nω-nitro-L-arginine, Ki = 84 μM), being the first examples of organometallic complexes able to inhibit the iNOS. These results seem to indicate that 99mTc(CO)3-labeled L-argininine analogues, namely NOS inhibitors, may hold potential for monitoring increased levels of iNOS in vivo.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...