Timescale for hygroscopic conversion of calcitemineral particles through heterogeneous reaction with nitric acid†
Abstract
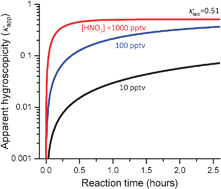
Atmospheric heterogeneous reactions can potentially change the hygroscopicity of atmospheric aerosols as they undergo chemical
- This article is part of the themed collection: Physical chemistry of aerosols

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...