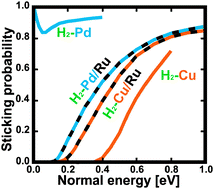
We present an extensive study based on the density functional theory (DFT) of the hydrogen dissociative adsorption on strained pseudomorphic monolayers of Cu or Pd deposited onto a Ru(0001) substrate. First, the full six-dimensional potential energy surfaces (PESs) are obtained by interpolation of the DFT ab initio calculations using the corrugation reducing procedure. The accuracy of these PESs is analyzed in detail. Then, the dissociative adsorption probability has been determined by means of six-dimensional (6D) quasi-classical dynamics simulations for both normal and off-normal incidence. Although H2 dissociation is known to be non activated on Pd(111) and strongly activated on Cu(111), we have found that it is activated on both Pd/Ru(0001) and Cu/Ru(0001). Surprisingly, the minimum activation energy for H2 dissociation is very similar on both pseudomorphic monolayers, ∼100 meV. In both cases, H2 dissociation occurs after the first encounter between the molecule and the surface (direct process) and, as expected, the adsorption probabilities follow, to a good approximation, normal energy scaling.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...