Maximum work in minimum time from a conservative quantum system
Abstract
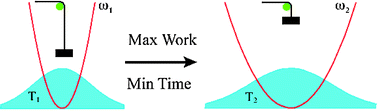
This paper considers the problem of obtaining maximum work from a conservative quantum system corresponding to a given change in an external parameter in the Hamiltonian. The example we present is a non-interacting collection of harmonic oscillators with a shared frequency ω which changes from a given initial to a given final value. The example is interesting for its role in experiments at ultra-low temperatures and for probing finite-time versions of the third law of thermodynamics. It is also the simplest system displaying quantum friction, which represents loss mechanisms in any reversible prelude to a thermal process. The example leads to a new type of availability. It is also the first example of a minimum time for transitions between thermal states of a thermodynamic system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...