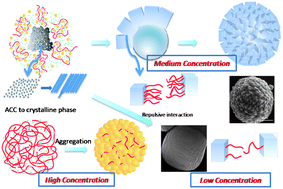
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is systematically investigated for the first time in regulating the CaCO3crystallization using a biomimetic gas-diffusion method. Monodisperse rosette-like calcite spherules in uniform size with their surfaces composed of rhombohedral subunits were synthesized in certain conditions. According to time-resolved experiment, the evolution of the crystal morphology was traced and the possible route in which rosette-like spherules form is suggested. We propose that the amorphous calcium carbonate precursors form initially and act as secondary nuclei, followed by the stacking of rhombohedral subunits in partial rather than complete superposition between each other due to the electrostatic repulsive interactions between the polyanion chains adsorbed on the blocks, which results in the final rosette-like morphology. Mineralization experiments in CMC solutions with different concentrations were also carried out and the results obtained at no higher than 1 g L−1 further prove the above mechanism from the fact that the extent of the polymer influence decreases proportionally with concentration, i.e. the degree of superposition of the building blocks becomes larger by decreasing the CMC concentration. In contrast, in a higher polymer concentration of 5 g L−1, another aggregation way from nanoparticles is adopted. In addition, the influence of the initial calcium ion concentration and the chain length of CMC on the crystal morphology were also investigated. The present investigation on the influence of CMC on CaCO3crystallization not only provides for the formation mechanisms of the rosette-like calcite spherules but also leads to a new possible route to fabricate new materials which can be used in many industrial areas.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...