Model systems for flavoenzyme activity: an investigation of the role functionality attached to the C(7) position of the flavin unit has on redox and molecular recognition properties†‡
Abstract
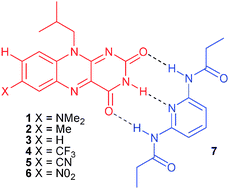
We describe the role functionality attached to the C(7) position of a family of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...