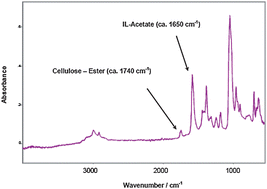
An ATR-FT-IR-based method was applied to measure the degree of substitution (DS) of esterified cellulose. The strategy makes use of the capability of certain ionic liquids (ILs) to dissolve cellulose derivatives. To avoid high viscosity that could hamper the correct measurement, a mixture of DMSO/IL (2 : 1, w/w) was applied. In ATR-FT-IR, ester absorption appeared at ca. 1740 cm−1, whereas carboxylic groups (acids) did at ca. 1710 cm−1, and carboxylates at ca. 1650 cm−1. The overlap of absorbances (ester–carboxylic acid) was circumvented by adding base equivalents, i.e.monoethanolamine (MEA). The base converted all free carboxylic acids in MEA-carboxylates, thus shifting the ATR-FT-IR integrated absorbance of carboxylic acid from ca. 1710 cm−1 to ca. 1650 cm−1, whereas the ester absorbance remained at ca. 1740 cm−1. Therefore a proper separation among peaks (esters vs. carboxylates) was achieved, and quantitative measurements of DS (ester) were obtained even when excesses of carboxylic acids were present (which can be analogous to actual reaction conditions for the esterification of cellulose). The high versatility of ILs suggests that the herein reported strategy might be rapidly extended to the study of other polymeric derivatives (i.e. containing carboxylic acids, etc.), by choosing the correct tailor-made IL, as well as to other analytic techniques.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...